What we know about muscle pain relief with the use of naturally occurring spice Ginger
March 4, 2021
Are you susceptible to develop Urinary Infection?
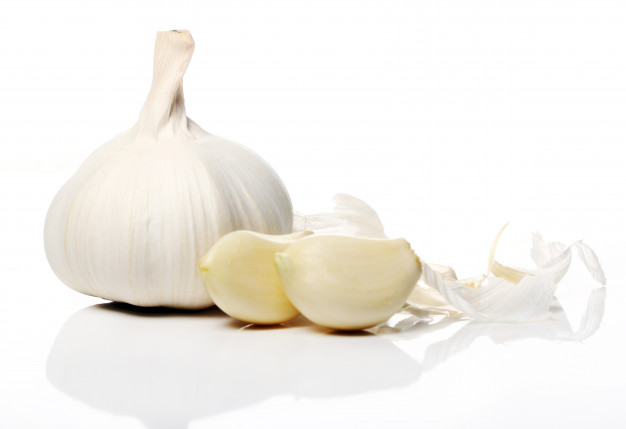
March 29, 2021Dietary factors can play a key role in preventing various disease conditions. Garlic (Botanical name: Allium sativum L.) is a common herb consumed worldwide as functional food and traditional remedy for prevention of infectious diseases since ancient times.
[Functional foods also called nutraceuticals are foods that offer health benefits beyond their nutritional value.]
For thousands of years garlic has been popular for its medicinal properties and throughout history many different cultures have recognized the potential use of garlic for prevention and treatment of different diseases. It has been used to treat various disease conditions such as cold, flu and other respiratory infections, earaches, diarrhea, constipation, parasitic infections and even some chronic and deadly diseases.
Moreover, various scientific studies have shown that the major active components of garlic are its organosulfur compounds; such as allicin, ajoene, alliin etc. Garlic due to its bioactive constituents exhibit antioxidants properties (antioxidants are substances that can prevent or slow the damaged to cells caused by unstable molecules produced in the body), anti-inflammatory effects (helps reduce inflammation), immunomodulatory properties (immunomodulators are substances that help to regulate the immune system), antiviral activity (antiviral agents are used for the treatment or control of viral infections. Viruses are tiny particles. They consist of a shell made-up of protein which envelops the genetic material along with the enzymes or chemicals for their replication. A virus must infect some kind of cell to replicate) and antimicrobial effects (substances that can kill or slow the spread of microorganisms).
It has been reported through pre-clinical (Research using animals to find out if a drug, procedure or treatment is likely to be useful) and clinical investigations (Clinical investigations determines the safety and effectiveness of medication, devices, diagnostic products and treatment regimens intended for human use) that garlic and its active ingredient, organosulfur compounds (OSCs) alleviate or help reduce a number of viral infections. However, so far there was no systemic review on its antiviral effects and the underlying molecular mechanisms; thus, recently researchers conducted a review to systematically summarize pre-clinical and clinical investigations on antiviral effects of garlic and its OSCs as well as to further analyze recent findings on the mechanisms that contribute to these antiviral actions.
[Systemic review aims to identify, evaluate and summarize the findings of all relevant individual studies over health-related issue].
To conduct the review PubMed, Cochrane library, Google Scholar and Science Direct databases were searched and articles up to June 2020 were included in this review. The pre-clinical data demonstrated that garlic and its OSCs have potential antiviral activity against different human, animal and plant pathogenic (disease causing) viruses through mechanisms such as; blocking viral entry into host cells, and inhibiting different viral enzymes. Furthermore, the alleviation of viral infection was also shown to link with immunomodulatory effects of garlic and its OSCs.
Moreover, the clinical studies further demonstrated a prophylactic (preventive) effect of garlic in prevention of widespread viral infections in humans through enhancing the immune response (Body’s defensive mechanisms against disease causing organisms and harmful substances).
Thus, researchers concluded that this review highlights that garlic possesses significant antiviral activity and can be used prophylactically in prevention of viral infections.
REFERENCE:
Antiviral potential of garlic (Allium sativum) and its organosulfur compounds: A systematic update of pre-clinical and clinical data
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0924224420305641
Bioactive Compounds and Biological Functions of Garlic (Allium sativum L.)


