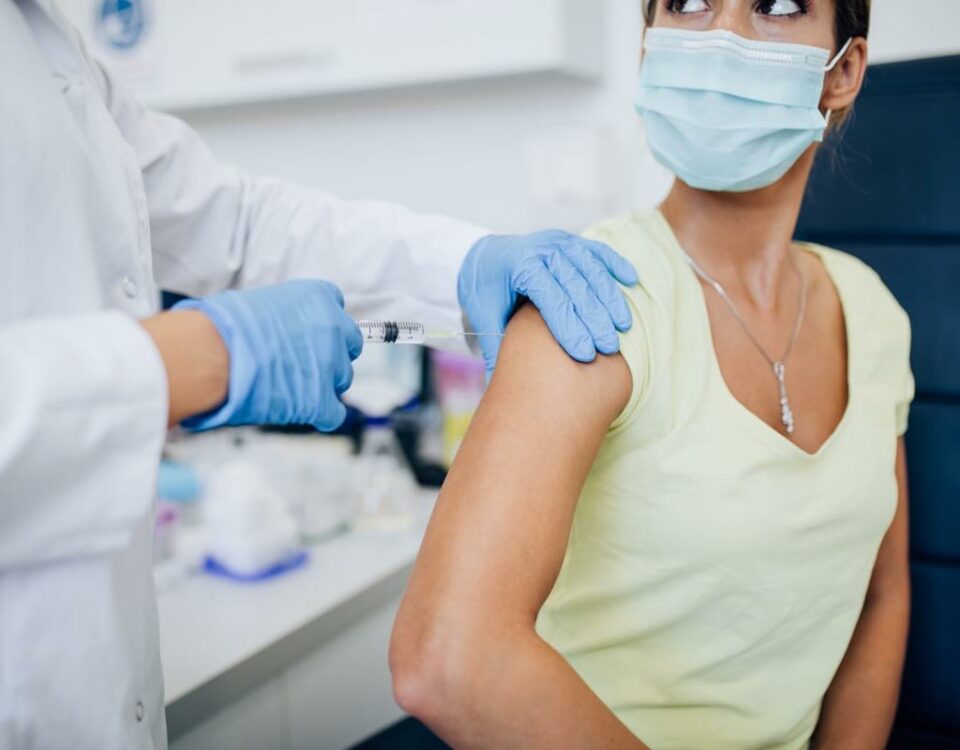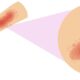
What do we know about ‘Urticaria’
February 4, 2022
Relationship between Healthy and Unhealthy Obesity types and occurrence of Hypertension.
May 14, 2022Reviewer: Dr. Abid
Depression is a very common mental health condition; it is one of the leading causes of health-related disease burden and it is also one of the major causes of disability worldwide. Furthermore, premature mortality or death from other disease conditions is linked to depressive mental state of an individual, and it is also associated with increased risk of suicidal tendencies.
Depression is classified as a mood disorder and manifests as persistent feeling of sadness, loss or anger, disturbed sleep patterns, reduced energy, low self-esteem, body aches, increased pain perception and suicidal thoughts etc. This mental state interferes with a person’s everyday activities and can also affect interpersonal relationships.
In general patients of depression are managed with medicines and counselling but scientific evidence suggests that physical activity or exercise is one of the effective behavioural interventions that can help manage depression.
How exercise helps in managing symptoms of depression?
Though the precise mechanism for antidepressant effects of exercise are still unclear but scientific data consistently points to a relationship between exercise and depression.
Health expert hypothesize and suggest several physiological and psychological mechanisms that explain the positive impacts of exercise in reducing symptoms of depression. Some of these mechanisms may include:
- Exercise causes release of feel good chemicals called ‘endorphins’ and several other chemicals in the brain which can help ease the symptoms of depression by restoring the sense of well-being in an individual and also by improving brain functions.
- Rise in the core body temperature following exercise can also be responsible for reducing symptoms of depression by causing an overall feeling of relaxation and reduction in muscular tension.
- Physical activity causes distraction from worries and negative thoughts and thus can help coping with symptoms of depression.
- Exercise improves one’s feeling of self efficacy which is described as the belief that one possesses the necessary skills to complete a task; thus this belief helps in coping with depression.
A systemic review and Meta-analysis to assess the association between physical activity and risk of depression
A team of researchers have conducted a systemic-review and meta-analysis to assess the dose-response association between physical activity and risk of depression.
A dose-response relationship means that increasing level of exposure i.e. exercise in this case, is associated with either an increasing or a decreasing risk of outcome which is depression.
A systematic review is a complex piece of research that aims to identify, select and compile all research published on a particular question or topic, for the topic of concern was is there a relationship between exercise and depression?
Meta-analysis is the use of statistical methods to summarize the results of multiple studies on a topic of interest.
The analysis included a total of 15 studies from data sources of Pub Med, SCOPUS, Web of Science, PsycINFO; and the reference lists of systemic reviews retrieved by a systematic search up to December 11, 2020, with no language limits. The date of the search was November 12, 2020.
Results and conclusions of the studies
It was observed through a number of studies that relatively small doses of physical activity were associated with substantially lower risks of depression; adults meeting physical activity recommendations (equivalent to 2.5 h/wk of brisk walking) had lower risk of depression, compared with adults reporting no physical activity. The systemic review and meta-analysis of associations between physical activity and depression suggests significant mental health benefits from being physically active, even at levels below the public health recommendations. Furthermore, the researchers recommend that health practitioners should therefore encourage any increase in physical activity to improve mental health.
REFERENCE:
Association between Physical Activity and Risk of Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapsychiatry/fullarticle/2790780
The Benefits of Exercise for the clinically Depressed